Idemitsu Tanker Co., Ltd., IINO Kaiun Kaisha, Ltd. (IINO Lines), Nippon Yusen Kabushiki Kaisha (NYK), and Nihon Shipyard Co., Ltd. are pleased to announce that the consortium the companies established on 26 January 2024 for the joint research and development of an eco-friendly very large crude oil carrier (VLCC) has produced a design concept for Japan’s first Malacca Max (*1) type VLCC to use methanol as alternative fuel.

Principal Particulars of Vessel:
| Length Overall | Max 339.5 m |
| Breadth | 60.0 m |
| Depth | 28.6 m |
| Scantling Draught | 21.0 m |
| Deadweight at Scantling Draught | Approx. 309,400 t |
| Fuel | Methanol and heavy oil |
| Others | Equipped with a shaft generator Able to equip with a Rotor Sail wind propulsion system |
To provide power while sailing, the Vessel will be equipped with a shaft generator (*2) and the latest dual-fuel main engine that can use methanol and heavy oil as fuel. A wind propulsion system (*3) will be optional.
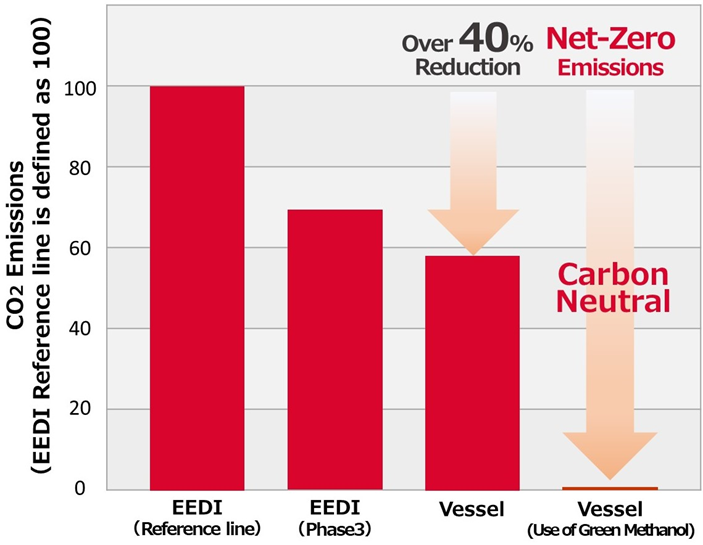
As a result, the Vessel can achieve a CO2 reduction of more than 40% compared to the reference line against the Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) regulation (*4), clearing Phase 3 (reduction of more than 30% compared to the reference line), which will apply from 2025.
Methanol is expected to contribute to the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction strategy by reducing CO2 emissions by approximately 15% compared to the use of conventional fuel oil. In addition, the use of green methanol, such as bio-methanol produced from biomass and synthetic methanol (e-methanol) produced using hydrogen from renewable energy sources and captured CO2, makes it possible to reduce CO2 emissions to net zero (*5).
