Global shipping was in chaos even before the Suez blockage. Shortages and higher prices loom.
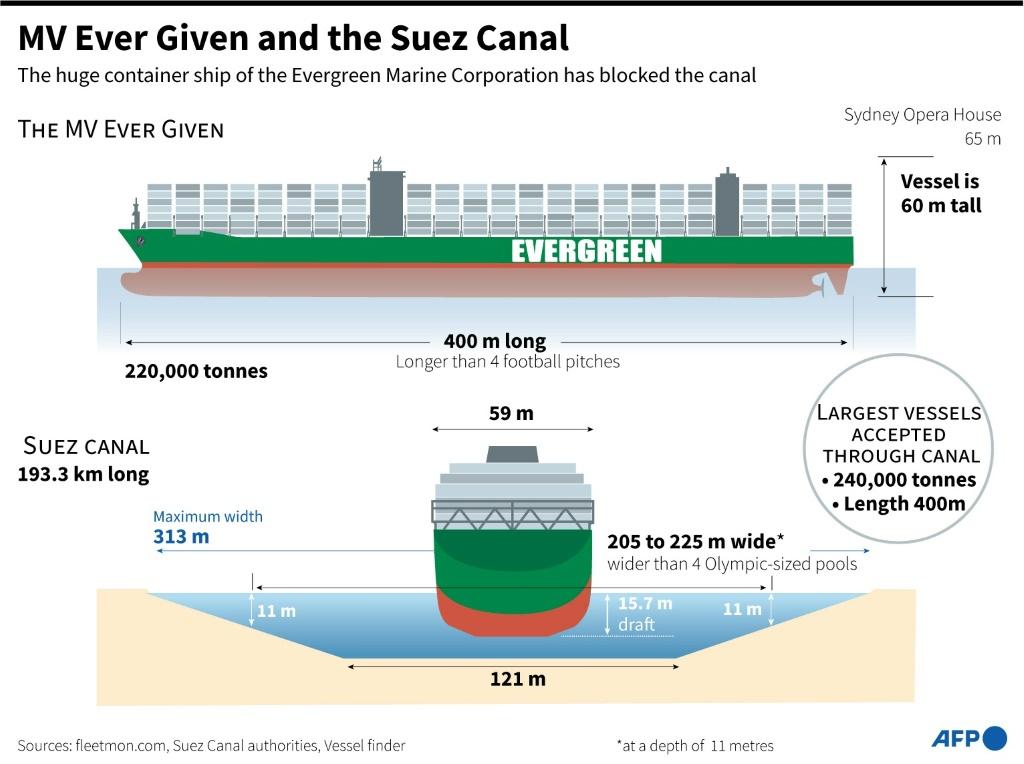
One of the world's most vital trade arteries has been blocked by a quarter-mile-long container ship Ever Given, creating a traffic jam that has ensnared over 200 vessels and could take weeks to clear.
But even before the Ever Given ran aground in the Suez Canal earlier this week, global supply chains were being stretched to the limits, making it much more expensive to move goods around the world and causing shortages of everything from exercise bikes to cheese at a time of unprecedented demand.
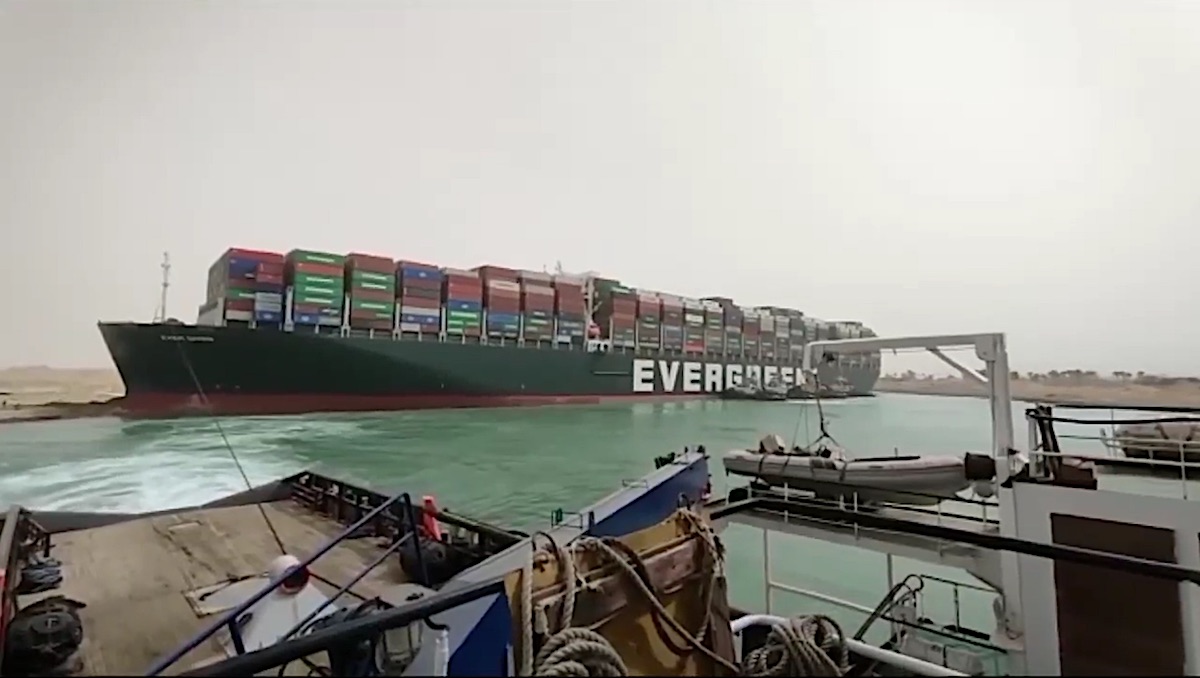

At least 8 vessels are engaged in the refloating efforts that continue in place. The following video simulation shows all attempts made on Thursday, 25th of March 2021.
A prolonged closure of the key route between West and East could make matters much worse. Costly delays or diversions to longer routes will heap pressure on businesses that are already facing container shortages, port congestion and capacity constraints.
The grounding of the Ever Given is delaying shipments of consumer goods from Asia to Europe and North America, and agricultural products moving in the opposite direction. As of Friday, some 237 vessels, including oil tankers and dozens of container ships, were waiting to transit the canal, which handles about 12% of global trade.
"There's been a great convergence of constraints in supply chains like I've never seen before," said Bob Biesterfeld, the CEO of C.H. Robinson, one of the world's largest logistics firms. The bottlenecks are widespread, affecting transport by air, ocean and road, Biesterfeld told CNN Business in an interview. "It really has been unprecedented."
FEARS BLOCKAGE COULD LAST WEEKS
Egypt's Suez Canal Authority has said between 15,000 and 20,000 cubic metres of sand would have to be removed in order to reach a depth of 12-16 metres and refloat the ship.
Egyptian President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi's seaports adviser, Mohab Mamish, told late Thursday that "maritime navigation will resume again within 48-72 hours, maximum".
"I have experience with several rescue operations of this kind and as the former chairman of the Suez Canal Authority, I know every centimetre of the canal," said Mamish, who oversaw the recent expansion of the waterway.
However, salvage experts had warned earlier on Thursday the shutdown could last days or even weeks.

Smit Salvage has in the past worked on the wrecks of Russian nuclear submarine Kursk and Italian cruise ship Costa Concordia.
Evergreen has asked Smit Salvage and Japanese company Nippon Salvage to put in place a "more effective plan" to refloat the ship.
Smit Salvage said it was deploying a team to the site Thursday to assess what it would take to dislodge the Panama-flagged vessels.
Crude prices jumped by almost six per cent on Wednesday in response to the Suez Canal blockage. But they tumbled on Thursday, at one point completely wiping out the earlier gains.
"Oil prices corrected excess gains that accumulated from the Suez Canal blockage as the disruption's effect is likely not one that will last too long," said Bjornar Tonhaugen of energy consultancy Rystad.
Freight costs soaring
More than 80% of global trade by volume is moved by sea, and the disruptions are adding billions of dollars to supply chain costs. Globally, the average cost to ship a 40-foot container shot up from $1,040 last June to $4,570 on March 1, according to S&P Global Platts.
Those costs add up. In February, container shipping costs for seaborne US goods imports totaled $5.2 billion, compared to $2 billion during the same month in 2020, according to S&P Global Panjiva.
These expenses could soon mean higher prices for consumers, adding upward pressure to rising inflation — a nightmare scenario for Wall Street, which is already fearful that a spike in prices could force the Federal Reserve to hike interest rates sooner than expected.
"At the moment a lot of these costs are within the supply chains," said Chris Rogers, a research analyst at S&P Global Panjiva. "I think it's inevitable that it will be passed on to consumers — it's just going to take time," he added.
The coronavirus wreaked havoc on global supply chains last year, as lockdowns temporarily closed factories and disrupted the normal flow of trade. Economic activity slowed dramatically at the start of the pandemic, and the rapid rebound in trade volumes that followed caught companies off guard.
A pickup in manufacturing and seemingly insatiable demand from housebound consumers for goods such as televisions, furniture and exercise bikes has stretched suppliers and made it difficult for consumers to find the products they'd like to buy.
Manufacturers have also struggled to secure crucial components. Major carmakers, including Ford (F) and Volkswagen (VLKAF), have been forced to idle factories because of a shortage of computer chips caused by high demand for smartphones, gaming systems and other tech gadgets.
"One year ago, global trade slowed to a crawl as the Covid-19 pandemic first hit China and then spread worldwide," Gene Seroka, executive director at the Port of Los Angeles, said in a presentation this month. "Today, we are in the seventh month of a historic import surge, driven by unprecedented demand by American consumers," he added.
US seaborne imports were nearly 30% higher in February than the same month last year and 20% up on February 2019, according to S&P Global Panjiva.
The import surge in the United States and elsewhere has led to a worldwide container shortage. Everything from cars and machinery to apparel and other consumer staples are shipped in these metal boxes. The factories that make them are mostly in China and many of them closed early in the pandemic, slowing down the rate at which new capacity was coming on stream, according to Rogers.
Containers are in all the wrong places
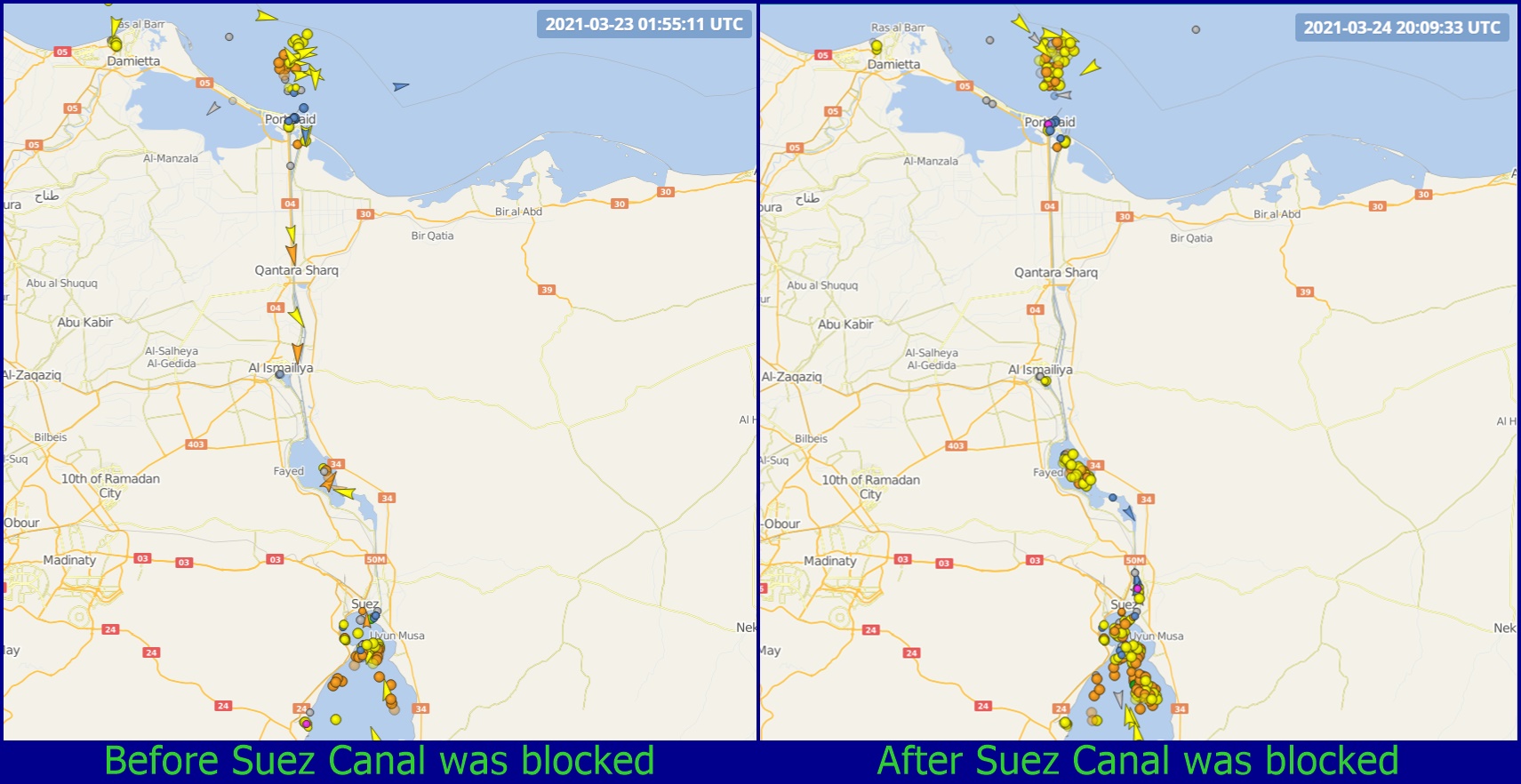
China's exports recovered fairly quickly compared to the rest of the world. At the same time, major shipping lines had canceled dozens of sailings to respond to the earlier lull in trade. The result was that empty containers piled up in all the wrong places and couldn't meet the sudden demand in Europe and North America for Asia-made goods.
Hapag-Lloyd (HPGLY), one of the world's largest container shipping lines, has deployed about 52 additional vessels just to move hundreds of thousands of empty containers to where they're needed most. In more normal times, there would be fewer than 10.
"That's in reality about a ship a week that's doing nothing more than moving empty containers," CEO Rolf Habben Jansen told investors on a call last week.
The influx of imports has compounded problems at choked up ports, which are contending with labor shortages due to Covid-19 and a slowdown in operations caused by social distancing measures and quarantines.
On Wednesday, there were two dozen vessels at anchor awaiting entry into either the Port of Los Angeles or the neighboring Port of Long Beach, according to Port of Los Angeles spokesperson, Phillip Sanfield.
"At the Port of Los Angeles, we are actively working on an additional 17 container ships," Sanfield told CNN Business. "Pre-pandemic, we would be working about 10 container ships with no container ships waiting to enter."
The port processed the equivalent of nearly 800,000 20-foot containers last month — the busiest February in its 114-year history.
Higher prices on the way
Companies have so far said very little about how they plan to respond to soaring freight rates but there are early signs that import prices are rising. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, US import prices experienced their largest monthly increase in January since March 2012.
"We anticipate strong demand from consumers to continue over the next couple of months and don't see meaningful change in capacity over that short time period," said Biesterfeld.
The cost to move goods by air, ocean, truck and train is now "structurally up" on 2019 and contracts reflect that, he added. "I do think the costs are real and eventually will manifest themselves for consumers," he said.
The extent to which this feeds through to consumer prices will vary from one product to the next. Goods that rely more heavily on imported components will likely cost more. At the same time, if the cost of imported goods rises significantly or these products become less readily available, that could give domestic producers more leeway to increase prices, said Joanna Konings, a senior economist at ING.
Commerzbank analysts said in a note to clients on Friday that the Suez snarl up could cause oil to become more expensive for consumers because of higher tanker rates as a result of the incident.
For Aston Chemicals, the cost increases were so severe that the only option was to pass them on to their customers: businesses that make everyday products such as shampoos, moisturizers and cosmetics.
If those companies in turn decide to hike prices for their customers, in this case retailers, consumers could start to feel the pinch soon, said Konings.
Source: CNN
Related news:
- Suez Canal Reopens for traffic after Ever Given was Refloated
- “Challenge still ahead” to free container ship EVER GIVEN in Suez Canal
- Ever Given ship Successfully Refloated in Suez Canal, Video shows her floating
- UPDATE 8 on Ever Given - High tide offers Best chance of moving Ever Given tonight
- UPDATE7: Japanese owner Shoei Kisen of stranded Suez Canal ship aims to free vessel on Saturday
- UPDATE 5 on Suez Canal Blocked by Ever Given - Steps to free the Ever Given?
- UPDATE 4 on Suez Canal Blocked by Ever Given - Japanese owner apologises, Refloating efforts Continue
- UPDATE 3 on Suez Canal Blocked by Ever Given - Photos and Videos
- UPDATE 2: Suez Canal Blocked by Huge container ship; Video simulation of the controversial track
- UPDATE 1: Suez Canal Blocked by Huge container ship; The first attempt to refloat the vessel - unsuccessful
- Suez Canal Blocked by Huge container ship Ever Given